- Router>: User mode = Limited to basic monitoring commands
- Router#: Privileged mode (exec-level mode) = Provides access to all other router commands
- Router(config)#: global configuration mode = Commands that affect the entire system
- Router(config-if)#: interface mode = Commands that affect interfaces
- Router(config-subif)#: subinterface mode = Commands that affect subinterfaces
- Router(config-line)#: line mode = Commands that affect in lines modes (console, vty, aux…)
- Router(config-router)#: router configuration mode
1
|
Switch(config)# hostname SW1
|
Konfigurasi passwords:
1
2
|
SW1(config)# enable secret cisco ! MD5 hash
SW1(config)# enable password notcisco ! Clear text
|
Securing console port:
1
2
3
|
SW1(config)# line con 0
SW1(config-line)# password cisco
SW1(config-line)# login
|
Securing terminal lines:
1
2
3
|
SW1(config)# line vty 0 4
SW1(config-line)# password cisco
SW1(config-line)# login
|
Encrypting passwords:
1
|
SW1(config)# service password-encryption
|
Konfigurasi banners:
1
2
3
4
5
|
SW1(config)# banner motd $
-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-
UNAUTHORIZED ACCESS IS PROHIBITED
-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-
$
|
Giving the switch an IP address:
1
2
3
|
SW1(config)# interface vlan 1
SW1(config-if)# ip address 172.16.1.11 255.255.255.0 ! or DHCP
SW1(config-if)# no shutdown
|
Setting the default gateway:
1
|
SW1(config)# ip default-gateway 172.16.1.1
|
Saving configuration:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
SW1# copy running-config startup-config
Destination filename [startup-config]? ! Press enter to confirm file name.
Building configuration…
[OK]
! Short for write memory.
SW1# wr
Building configuration…
[OK]
|
Working environment:
1
2
3
4
5
|
SW1(config)# no ip domain-lookup
SW1(config)# line vty 0 4
SW1(config-line)# history size 15
SW1(config-line)# exec-timeout 10 30
SW1(config-line)# logging synchronous
|
Konfigurasi switch to use SSH:
- Configure DNS domain name:
1
|
SW1(config)# ip domain-name example.com
|
- Configure a username and password:
1
|
SW1(config)# username admin password cisco
|
- Generate encryption keys:
1
2
|
SW1(config)# crypto key generate rsa
How many bits in the modulus [512]: 1024
|
- Define SSH version to use:
1
|
SW1(config)# ip ssh version 2
|
- Enable vty lines to use SSH:
1
2
3
4
|
SW1(config)# line vty 0 4
SW1(config-line)# login local
! You can set vty lines to use only telnet or only ssh or both as in the example.
SW1(config-line)# transport input telnet ssh
|
Aliases:
1
2
3
|
SW1(config)# alias exec c configure terminal
SW1(config)# alias exec s show ip interface brief
SW1(config)# alias exec sr show running-config
|
Description, speed and duplex:
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
SW1(config)# interface fastEthernet 0/1
SW1(config-if)# description LINK TO INTERNET ROUTER
SW1(config-if)# speed 100 ! Options: 10, 100, auto
! The range keyword used to set a group of interfaces at once.
SW1(config)# interface range fastEthernet 0/5 – 10
SW1(config-if-range)# duplex full (options: half, full, auto)
|
- Shows information about the switch and its interfaces, RAM, NVRAM, flash, IOS, etc.
1
|
SW1# show version
|
- Shows the current configuration file stored in DRAM.
1
|
SW1# show running-config
|
- Shows the configuration file stored in NVRAM which is used at first boot process.
1
|
SW1# show startup-config
|
- Lists the commands currently held in the history buffer.
1
|
SW1# show history
|
- Shows an overview of all interfaces, their physical status, protocol status and ip address if assigned.
1
|
SW1# show ip interface brief
|
- Shows detailed information about the specified interface, its status, protocol, duplex, speed, encapsulation, last 5 min traffic.
1
|
SW1# show interface vlan 1
|
- Shows the description of all interfaces
1
|
SW1# show interfaces description
|
- Shows the status of all interfaces like connected or not, speed, duplex, trunk or access vlan.
1
|
SW1# show interfaces status
|
- Shows the public encryption key used for SSH.
1
|
SW1# show crypto key mypubkey rsa
|
- Shows information about the leased IP address (when an interface is configured to get IP address via a dhcp server)
1
|
SW1# show dhcp lease
|
[CCNA] Rangkuman konfigurasi Cisco #2
Konfigurasi port security:
- Make the switch interface as access port:
1
|
SW1(config-if)# switchport mode access
|
- Enable port security on the interface:
1
|
SW1(config-if)# switchport port-security
|
- Specify the maximum number of allowed MAC addresses:
1
|
SW1(config-if)# switchport port-security maximum 1
|
- Define the action to take when violation occurs:
1
|
SW1(config-if)# switchport port-security violation shutdown ! options: shutdown, protect, restrict
|
- Specify the allowed MAC addresses:
1
|
SW1(config-if)# switchport port-security mac-address 68b5.9965.1195 ! options: H.H.H, sticky
|
Verify and troubleshoot port security:
- Shows the entries of the mac address table:
1
|
SW1# show mac-address-table
|
- Overview of port security of all interfaces:
1
|
SW1# show port-security
|
- Shows detailed information about port security on the specified interface:
1
|
SW1# show port-security interface fa0/5
|
Konfigurasi VLANs:
- Create a new VLAN and give it a name:
1
2
|
SW1(config)# vlan 10
SW1(config-vlan)# name SALES
|
- Assign an access interface to access a specific VLAN:
1
2
3
|
SW1(config)# interface fastEthernet 0/5
SW1(config-if)# switchport mode access
SW1(config-if)# switchport access vlan 10
|
Konfigurasi an auxiliary VLAN for cisco IP phones:
1
2
3
4
|
SW1(config)# interface fastEthernet 0/5
! accessing vlan 10 (data) and 12 (VoIP)
SW1(config-if) #switchport access vlan 10
SW1(config-if) #switchport voice vlan 12
|
Konfigurasi Trunks:
1
2
3
|
SW1(config)# interface fastEthernet 0/1
SW1(config-if)# switchport mode trunk ! options: access, trunk, dynamic auto, dynamic desirable
SW1(config-if)# switchport trunk allowed vlan add 10 ! options: add, remove, all, except
|
Securing VLANs and Trunking:
- Administratively disable unused interfaces:
1
|
SW1(config-if)# shutdown
|
- Prevent trunking by disabling auto negotiation on the interface:
1
2
|
SW1(config-if)# nonegotiate ! or hardcode the port asan access port
SW1(config-if)# switchport mode access
|
- Assign the port to an unused VLAN:
1
|
SW1(config-if)# switchport access vlan 222
|
Konfigurasi VTP:
- Configure VTP mode:
1
|
SW1(config)# vtp mode server ! options: server, client, transparent
|
- Configure VTP domain name:
1
|
SW1(config)# vtp domain EXAMPLE ! case-sensitive
|
- Configure VTP password (optional):
1
|
SW1(config)# vtp password cisco ! case-sensitive
|
- Configure VTP pruning (optional):
1
|
SW1(config)# vtp pruning ! only works on VTP servers
|
- Enable VTP version 2 (optional):
1
|
SW1(config)# vtp version 2
|
Verify and troubleshoot VLANs and VTP:
- Lists information about administrative setting and operation status of interface:
1
|
SW1# show interfaces if switchport
|
- Lists all the trunk ports on a switch including the trunk allowed VLANs:
1
|
SW1# show interfaces trunk
|
- Lists information about the VLANs:
1
|
SW1# show vlan {brief | id | name | summary}
|
- Lists VTP configuration (mode, domain-name, version, etc) and revision number:
1
|
SW1# show vtp status
|
- Shows the VTP password:
1
|
SW1# show vtp password
|
STP optimization:
- Hard coding the root bridge (changing bridge priority):
1
2
3
4
|
SW1(config)# spanning-tree vlan 1 root primary
SW1(config)# spanning-tree vlan 1 root secondary
! Priority must be a multiply of 4096
SW1(config)# spanning-tree [vlan 1]priority 8192
|
- Changing the STP mode:
1
|
SW1(config)# spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst ! options: mst, pvst, rapid-pvst
|
- Enabling portfast and BPDU guard on an interface:
1
2
|
SW1(config-if)# spanning-tree portfast
SW1(config-if)# spanning-tree bpduguard enable
|
- Changing port cost:
1
|
SW1(config-if)# spanning-tree [vlan 1] cost 25
|
- Bundling interfaces into an etherchannel:
1
|
SW1(config-if)# channel-group 1 mode on ! options: auto, desirable, on
|
STP verification and troubleshooting:
- Shows detailed info about STP state:
1
|
SW1# show spanning-tree
|
- Shows STP info only on a specific port:
1
|
SW1# show spanning-tree interface fa0/2
|
- Shows STP info only for a specific VLAN:
1
|
SW1# show spanning-tree vlan 1
|
- Shows info about the root switch:
1
|
SW1# show spanning-tree [vlan 1] root
|
- Shows info about the local switch:
1
|
SW1# show spanning-tree [vlan 1] bridge
|
- Show the state of the etherchannels:
1
|
SW1# show etherchannel 1
|
- Provides informational messages about the changes in the STP topology:
1
|
SW1# debug spanning-tree events
|
Enabling or disabling CDP:
- Enabling CDP globally on a switch:
1
|
SW1(config)# cdp run
|
- Disabling CDP on a given interface:
1
|
SW1(config-if)# no cdp enable
|
Using CDP for network verification and troubleshooting:
- Shows global information about CDP itself:
1
|
SW1# show cdp
|
- Shows information about CDP on a specific interface:
1
|
SW1# show cdp interface fa0/2
|
- Shows information about the directly connected cisco devices including interfaces names capabilities:
1
|
SW1# show cdp neighbors
|
- Shows detailed information about the neighboring cisco devices including device address and version of IOS they run:
1
2
3
|
SW1# show cdp neighbors detail
! OR
SW1# show cdp entry *
|
- Shows detailed information about the specified entry only:
1
|
SW1# show cdp entry SW2
|
[CCNA] Rangkuman konfigurasi Cisco #3
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
Router(config)# hostname R1
R1(config)# enable secret cisco
R1(config)# line con 0
R1(config-line)# password cisco
R1(config-line)# login
R1(config-line)# logging synchronous
R1(config-line)# exec-timeout 30 0
R1(config-line)# exit
R1(config)# line vty 0 4
R1(config-line)# password cisco
R1(config-line)# login
R1(config-line)# logging synchronous
R1(config-line)# exec-timeout 30 0
R1(config-line)# exit
R1(config)# line aux 0
R1(config-line)# password cisco
R1(config-line)# login
R1(config-line)# logging synchronous
R1(config-line)# exec-timeout 30 0
R1(config-line)# exit
R1(config)# banner motd $
-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-
UNAUTHORIZED ACCESS IS PROHIBITED
-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-
$
R1(config)# alias exec c configure terminal
R1(config)# alias exec s show ip interface brief
R1(config)# alias exec sr show running-config
R1(config)# no ip domain-lookup
R1(config)# service password-encryption
R1(config)# ip domain-name example.com
R1(config)# username admin password cisco
R1(config)# crypto key generate rsa
How many bits in the modulus [512]: 1024
R1(config)# ip ssh version 2
R1(config)# line vty 0 4
R1(config-line)# login local
R1(config-line)# transport input telnet ssh
|
Konfigurasi router interfaces:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
R1(config)# interface fastEthernet 0/0
R1(config-if)# description LINK TO LOCAL LAN THROUGH SW1
R1(config-if)# ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)# no shutdown
R1(config-if)# exit
R1(config)# interface serial 0/1/0
R1(config-if)# description WAN CONNECTION TO R2
R1(config-if)# ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252
R1(config-if)# clock rate 128000
R1(config-if)# no shutdown
|
Konfigurasi Router-On-Stick for vlanrouting:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
R1(config)# interface fastEthernet 0/0
R1(config-if)# no shutdown
R1(config)# interface fastEthernet 0/0.10
R1(config-subif)# encapsulation dot1q 10
R1(config-subif)# ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-subif)# interface fastEthernet 0/0.20
R1(config-subif)# encapsulation dot1q 20
R1(config-subif)# ip address 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0
|
- Using next hop:
1
|
R1(config)# ip route 10.1.2.0 255.255.255.0 10.1.128.1
|
- Using exit interface:
1
2
|
R1(config)# ip route 10.1.2.0 255.255.255.0 Serial 0/0
*Note: Exit interface can be used in point-to-point serial links.
|
1
|
R1(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 199.1.1.1
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
R1(config)# router rip
R1(config-router)# version 2
R1(config-router)# network 10.0.0.0 ! written as an original class A
R1(config-router)# no auto-summary
R1(config-router)# passive-interface serial 0/0
|
RIPv2 Verification:
- Shows information about the running routing protocol process:
1
|
R1# show ip protocols
|
- Shows the entire routing table:
1
|
R1# show ip route
|
- Shows routes learned via RIP only:
1
|
R1# show ip route rip
|
- Shows detailed information about the route to the specified destination network:
1
|
R1# show ip route 10.1.1.1
|
- Enter OSPF router configuration mode:
1
|
R1(config)# router ospf 10 ! 10 = process ID
|
- Configure one or more network commands to identify which interfaces will run OSPF:
1
2
3
|
R1(config-router)# network 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 0
R1(config-router)# network 172.16.8.0 0.0.7.255 area 0
R1(config-router)# network 192.168.1.254 0.0.0.0 area 1
|
- Configure router ID either (Optional):
1
|
R1(config-router)# router-id 1.1.1.1
|
Konfigurasi an IP address on a loopback interface:
1
2
|
R1(config)# interface loopback 0
R1(config-if)# ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
|
- Change Hello and Dead intervals per interface (Optional):
1
2
|
R1(config-if)# ip ospf hello-interval 2
R1(config-if)# ip ospf dead-interval 6
|
- Impact routing choices by tuning interface cost using one of the following ways (Optional):
1
|
R1(config-if)# ip ospf cost 55
|
Changing interface bandwidth:
1
|
R1(config-if)# bandwidth 128 ! in Kbps
|
Changing the reference bandwidth that used by OSPF to calculate the cost:
1
|
R1(config-router)# auto-cost reference-bandwidth 1000 ! in Mbps
|
- Disabling OSPF on a certain interface (Optional):
1
|
R1(config-router)# passive-interface serial 0/0
|
- Konfigurasi OSPF authentication (Optional):
1
|
R1(config-if)# ip ospf authentication null
|
Type 1 authentication (clear text):
1
2
|
R1(config-if)# ip ospf authentication
R1(config-if)# ip ospf authentication-key cisco
|
Type 2 authentication (md5):
1
2
|
R1(config-if)# ip ospf authentication message-digest
R1(config-if)# ip ospf message-digest-key 1 md5 cisco
|
- Configure maximum equal-cost paths (Optional):
1
|
R1(config-router)# maximum paths 6
|
OSPF verification:
- Shows information about the running routing protocol process:
1
|
R1# show ip protocols
|
- Shows the entire routing table:
1
|
R1# show ip route
|
- Shows routes learned via OSPF only:
1
|
R1# show ip route ospf
|
- Shows all neighboring routers along with their respective adjacency state:
1
|
R1# show ip ospf neighbors
|
- Shows all the information contained in the LSDB:
1
|
R1# show ip ospf database
|
- Shows detailed information about OSPF running on a specific interface:
1
|
R1# show ip ospf interfaces serial 0/0
|
- Enter EIGRP configuration mode and define AS number:
1
|
R1(config)# router eigrp 121 ! 121 = AS number
|
- Configure one or more network commands to enable EIGRP on the specified interfaces:
1
2
3
4
|
R1(config-router)# network 10.0.0.0
R1(config-router)# network 172.16.0.0 0.0.3.255
R1(config-router)# network 192.168.1.1 0.0.0.0
R1(config-router)# network 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255
|
- Disable auto summarization (Optional):
1
|
R1(config-router)# no auto-summary
|
- Disable EIGRP on a specific interface (Optional):
1
|
R1(config-router)# passive-interface serial 0/0
|
- Configure load balancing parameters (Optional):
1
2
|
R1(config-router)# maximum-paths 6
R1(config-router)# variance 4
|
- Change interface Hello and Hold timers (Optional):
1
2
|
R1(config-if)# ip hello-interval eigrp 121 3
R1(config-if)# ip hold-time eigrp 121 10
|
- Impacting metric calculations by tuning BW and delay of the interface (Optional):
1
2
|
R1(config-if)# bandwidth 265 ! in Kbps)
R1(config-if)# delay 120 ! tens of microseconds
|
EIGRP Authentication:
- Create an authentication key chain as follows:
1
|
R1(config)# key chain MY_KEYS
|
Create one or more keys giving them numbers:
1
|
R1(config-keychain)# key 1
|
Define the key value:
1
|
R1(config-keychain-key)# key-string1stKEY
|
Define the life time of the keys (optional):
1
2
|
R1(config-keychain-key)# send-lifetime [start time] [end time]
R1(config-keychain-key)# accept-lifetime [start time] [end time]
|
- Enable md5 authentication mode for EIGRP on the interface:
1
|
R1(config-if)# ip authentication mode eigrp121 md5
|
- Refer to the correct key chain to be used on the interface:
1
|
R1(config-if)# ip authentication key-chain eigrp121 MY_KEYS
|
EIGRP Verification:
- Shows routes learned via EIGRP only:
1
|
R1# show ip route eigrp
|
- Shows EIGRP neighbors and status:
1
|
R1# show ip eigrp neighbors
|
- Shows EIGRP topology table, including successor and feasible successor:
1
|
R1# show ip eigrp topology
|
- Shows interfaces that run EIGRP:
1
|
R1# show ip eigrp interfaces
|
- Lists statistics on numbers of EIGRP messages sent and received by the router:
1
|
R1# show ip eigrp traffic
|
[CCNA] Rangkuman konfigurasi Cisco #4
Access Control Lists:
Standard ACL: 1 – 99 and 1300 – 1999
- Use a remark to describe the ACL (Optional):
1
| R1(config)# access-list 1 remark ACL TO DENY ACCESS FROM SALES VLAN |
- Create the ACL, keeping the following in mind:
- ACL uses first-match logic.
- There is an implicit deny anyat the end of the ACL.
1
2
3
4
5
| R1(config)# access-list 2 deny 192.168.1.77R1(config)# access-list 2 deny 192.168.1.64 0.0.0.31R1(config)# access-list 2 permit 10.1.0.0 0.0.255.255R1(config)# access-list 2 deny 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255R1(config)# access-list 2 permit any |
- Enable the ACL on the chosen router interface in the correct direction (in or out):
1
| R1(config-if)# ip access-group 2 out |
- Using standard ACL to limit telnet and SSH access to a router:
1
2
| R1(config)# access-list 99 remark ALLOWED TELNET CLIENTSR1(config)# access-list 99 permit 192.168.1.128 0.0.0.15 |
Apply the ACL inbound the vty lines
1
2
| R1(config)# line vty 0 4R1(config-line)# access-class 99 in |
Extended ACL: 100 – 199 and 2000 – 2699
- Extended ACL should be placed as close as possible to the source of the packet.
- Extended ACL matches packets based on source & des.IP addresses, protocol, source & des. Port numbers andother criteria as well
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| R1(config)# access-list 101 remark MY_ACCESS_LISTR1(config)# access-list 101 deny iphost 10.1.1.1 host 10.2.2.2R1(config)# access-list 101 deny tcp 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 any eq 23R1(config)# access-list 101 deny icmp 10.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 anyR1(config)# access-list 101 deny tcphost 10.1.1.0 host 10.0.0.1 eq 80R1(config)# access-list 101 deny udphost 10.1.1.7 eq 53 anyR1(config)# access-list 101 permit ip any anyR1(config)# interface fastEthernet 0/0R1(config-if)# ip access-group 101 in |
Named ACL:
- Named ACLs use names to identify ACLs rather than numbers, and commands that permit or deny traffic are written in a sub mode called named ACL mode (nacl).
- Named ACL enables the editing of the ACL (deleting or inserting statements) by sequencing statements of the ACL.
- Named standard ACL:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| R1(config)# ip access-list standard MY_STANDARD_ACLR1(config-std-nacl)# permit 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255R1(config-std-nacl)# deny 10.2.2.2R1(config-std-nacl)# permit anyR1(config)# interface fastEthernet 0/1R1(config-if)# ip access-group MY_STANDARD_ACL out |
- Named extended ACL:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| R1(config)# ip access-list extended MY_EXTENDED_ACLR1(config-ext-nacl)# deny icmp 10.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 anyR1(config-ext-nacl)# deny tcphost 10.1.1.0 host 10.0.0.1 eq 80R1(config-ext-nacl)# permit ip any anyR1(config)# interface fastEthernet 0/1R1(config-if)# ip access-group MY_EXTENDED_ACL in |
- Editing ACL using sequence numbers:
1
2
3
4
| R1(config)# ip access-list extended MY_EXTENDED_ACLR1(config-ext-nacl)# no 20 ! Deletes the statement of sequence number 20R1(config)# ip access-list standard 99R1(config-std-nacl)# 5 deny 1.1.1.1 ! inserts a statement with sequence 5 |
Verifying ACLs:
- Shows all ACLs configured on a router with counters at the end of each statement:
1
2
3
| R1# show access-lists! ORR1# show ip access-list |
- Shows only the specified ACL:
1
| R1# show ip access-list 101 |
- Includes a reference to the ACLs enabled on that interface either in or out:
1
| R1# show ip interface f0/0 |
DHCP Server
- Define a DHCP pool and give it a name:
1
| R1(config)# ip dhcp pool MY_POOL |
- Define network and mask to use in this pool and the default gateway:
1
2
| R1(dhcp-config)# network 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0R1(dhcp-config)# default-router 192.168.1.1 |
- Define one or more DNS server (OPTIONAL):
1
| R1(dhcp-config)# dns-server 213.131.65.20 8.8.8.8 |
- Confine the lease time (OPTIONAL):
1
| R1(dhcp-config)lease 2 ! Days |
- Define one or more scopes of excluded (reserved) addresses (OPTIONAL):
1
2
| R1(config)# ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.1.1 192.168.1.100R1(config)# ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.1.200 192.168.1.254 |
DHCP Verification and Troubleshooting:
- Shows the status of the specified pool and the leased addresses from that pool:
1
| R1# show ip dhcp pool POOL_1 |
- Shows all the leased ip addresses from all configured DHCP pools:
1
| R1# show ip dhcp binding |
- Shows any conflicts that occurred:
1
| R1# show ip dhcp conflict |
[CCNA] Rangkuman konfigurasi Cisco #5
PPP Configuration:
1
2
| R1(config)# interface serial 0/0R1(config-if)# encapsulation ppp |
PPP Authentication:
CHAP:
- Configure the hostname:
1
| R1(config)# hostname ALPHA |
- Configure the name of the other end router and the shared password:
1
2
| ! The password used is shared password, that means it must be the same on both routersALPHA(config)# username BETA password XYZ |
- Enable CHAP authentication on the interface:
1
2
| ALPHA(config)# interface serial 0/0ALPHA(config-if)# ppp authentication chap |
PAP:
- Configure the hostname:
1
| R1(config)# hostname ALPHA |
- Configure the name of the other end router and the shared password:
1
| ALPHA(config)# username BETA password XYZ |
- Enable PAP authentication on the interface and define the username and password to be sent by PAP:
1
2
3
| ALPHA(config)# interface serial 0/0ALPHA(config-if)# ppp authentication papALPHA(config-if)# ppp pap sent-username ALPHA password XYZ |
PPP Verification and troubleshoot:
- Shows the encapsulation type and the control protocols of PPP:
1
| R1# show interface s0/0 |
- Useful for viewing the configuration of usernames and passwords used to authenticate PPP:
1
| R1# show running-config |
- Displays the authentication process of PPP in real time:
1
| R1# debug ppp authentication |
Frame Relay:
Multipoint (one subnet)
- Give the interface an ip address and enable Frame Relay encapsulation:
1
2
3
| R1(config)# interface serial 0/0R1(config-if)# ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.0R1(config-if)# encapsulation frame-relay (ietf) |
- Configure LMI signaling type: (Optional as discussed with ISP):
1
| R1(config-if)# frame-relay lmi-type ansi ! options: ansi, cisco, q933a |
- Configure Frame Relay mapping:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
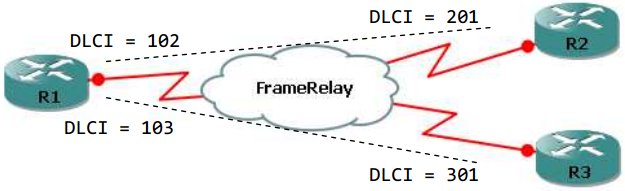
| R1(config-if)# frame-relay map ip 1.1.1.2 102 broadcast (ietf)R1(config-if)# frame-relay map ip 1.1.1.3 103 broadcastR2(config)# interface serial 0/0R2(config-if)# ip address 1.1.1.2 255.255.255.0R2(config-if)# encapsulation frame-relayR2(config-if)# frame-relay map ip 1.1.1.1 201 broadcastR2(config-if)# frame-relay map ip 1.1.1.3 201 broadcastR3(config)# interface serial 0/0R3(config-if)# ip address 1.1.1.3 255.255.255.0R3(config-if)# encapsulation frame-relayR3(config-if)# frame-relay map ip 1.1.1.1 301 broadcastR3(config-if)# frame-relay map ip 1.1.1.2 301 broadcast |
Point-to-point (different subnets; one subnet per subinterface)
- Enable Frame Relay encapsulation:
1
2
| R1(config)# interface serial 0/0R1(config-if)# encapsulation frame-relay |
- Give an ip address to a subinterface and configure its DLCI:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| R1(config)# interface serial 0/0.102 point-to-pointR1(config-subif)# ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.0R1(config-subif)# frame-relay interface-dlci 102R1(config)# interface serial 0/0.103 point-to-pointR1(config-subif)# ip address 2.2.2.1 255.255.255.0R1(config-subif)# frame-relay interface-dlci 103R2(config)# interface serial 0/0R2(config-if)# encapsulation frame-relayR2(config)# interface serial 0/0.201 point-to-pointR2(config-subif)# ip address 1.1.1.2 255.255.255.0R2(config-subif)# frame-relay interface-dlci 201R3(config)# interface serial 0/0R3(config-if)# encapsulation frame-relayR3(config)# interface serial 0/0.301 point-to-pointR3(config-subif)# ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.0R3(config-subif)# frame-relay interface-dlci 301 |
Frame Relay Verification and troubleshoot:
- Shows the encapsulation type:
1
| R1# show interfaces serial 0/0 |
- Lists PVC status information:
1
| R1# show frame-relay pvc |
- Lists DLCI to IP mapping:
1
| R1# show frame-relay map |
- Lists LMI status information:
1
| R1# show frame-relay lmi |
- Displays the content of LMI messages:
1
| R1# debug frame-relay lmi |
- Lists messages about certain Frame Relay events, including Inverse ARP messaeges:
1
| R1# debug frame-relay events |
Network Address Translation (NAT):
Static NAT:
- Define the outside and inside interfaces:
1
2
3
4
| R1(config)# interface serial 0/0R1(config-if)# ip nat outsideR1(config)# interface FastEthernet 1/1R1(config-if)# ip nat inside |
- Configure static NAT statement:
1
| R1(config)# ip nat inside source static 192.168.1.10 200.1.1.1 |
Dynamic NAT:
- Define the outside and inside interfaces
- Create an ACL that determines the IP addresses thatare allowed to be translated:
1
| R1(config)# access-list 3 permit 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 |
- Create a pool of public IP addresses:
1
| R1(config)# ip nat pool PUB 200.1.1.1 200.1.1.6 netmask 255.255.255.248 |
- Configure NAT statement:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| R1(config)# ip nat inside source list 3 pool PUB</pre><h4>NAT Overload (PAT):</h4><ul> <li>The same as dynamic NAT with the use of the overload keyword at the end of NAT statement:</li></ul><pre>1R1(config)# ip nat inside source list 3 pool PUB overload |
NAT verification and troubleshoot:
- Useful in viewing the configuration of NAT pool and the inside and outside interfaces:
1
| R1# show running-config |
- Displays access lists, including the one used for NAT:
1
| R1# show access-lists |
- Shows counters for packets and NAT table entries, as well as basic configuration information:
1
| R1# show ip nat stasitics |
- Displays the NAT table:
1
| R1# show ip nat translations |
- Clears all the dynamic entries in the NAT table:
1
| R1# clear ip nat translations * |
- Issues a log message describing each packet whose ip address is translated with NAT:
1
| R1# debug ip nat |
Sumber




 09.03
09.03
 Unknown
Unknown