Langkah pertama kita membuat suatu topologi jaringan seperti pada gambar di bawah ini :
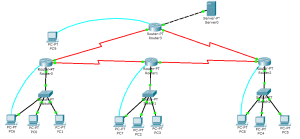
Dengan rancangan IP untuk menghubungkan jaringan :
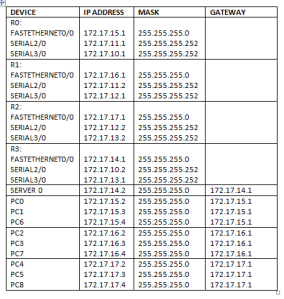
Lakukan konfigurasi pada PC sesuai IP pada tabel di atas.
Setelah itu kita akan melakukan konfigurasi pada router melalui PC yang sudah dihubungkan dengan conection console yaitu garis berwarna biru.
Setingan pada router 0 melalui PC:
Router>ena
Router#config
Configuring from terminal, memory, or network [terminal]?
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#interface fa0/0
Router(config-if)#ip address 172.17.15.1 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)#no shut
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up
Router(config-if)#exit
Router(config)#interface se2/0
Router(config-if)#ip address 172.17.11.1 255.255.255.252
Router(config-if)#clock rate 64000
Router(config-if)#no shut
Router(config-if)#exit
Router(config)#interface se3/0
Router(config-if)#ip address 172.17.10.1 255.255.255.252
Router(config-if)#clock rate 64000
Router(config-if)#no shut
Router(config-if)#exit
Router(config)#ip route 172.17.12.0 255.255.255.252 172.17.11.2
Router(config)#ip route 172.17.14.0 255.255.255.0 172.17.10.2
Router(config)#ip route 172.17.16.0 255.255.255.0 172.17.11.2
Router(config)#ip route 172.17.17.0 255.255.255.0 172.17.12.2
Router(config)#no shut
Setingan pada router 1 :
Router>ena
Router#config
Configuring from terminal, memory, or network [terminal]?
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#interface fa0/0
Router(config-if)#ip address 172.17.16.1 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)#no shut
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up
Router(config-if)#exit
Router(config)#interface se2/0
Router(config-if)#ip address 172.17.11.2 255.255.255.252
Router(config-if)#clock rate 64000
Router(config-if)#no shut
Router(config-if)#exit
Router(config)#interface se3/0
Router(config-if)#ip address 172.17.12.1 255.255.255.252
Router(config-if)#clock rate 64000
Router(config-if)#no shut
Router(config-if)#exit
Router(config)#ip route 172.17.15.0 255.255.255.0 172.17.11.1
Router(config)#ip route 172.17.17.0 255.255.255.0 172.17.12.2
Router(config)#ip route 172.17.10.0 255.255.255.252 172.17.11.1
Router(config)#ip route 172.17.14.0 255.255.255.0 172.17.10.2
Router(config)#no shut
Setingan pada router 2 :
Router>ena
Router#config
Configuring from terminal, memory, or network [terminal]?
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#interface fa0/0
Router(config-if)#ip address 172.17.17.1 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)#no shut
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up
Router(config-if)#exit
Router(config)#interface se2/0
Router(config-if)#ip address 172.17.12.2 255.255.255.252
Router(config-if)#clock rate 64000
Router(config-if)#no shut
Router(config-if)#exit
Router(config)#interface se3/0
Router(config-if)#ip address 172.17.13.2 255.255.255.252
Router(config-if)#clock rate 64000
Router(config-if)#no shut
Router(config-if)#exit
Router(config)#ip route 172.17.16.0 255.255.255.0 172.17.12.1
Router(config)#ip route 172.17.14.0 255.255.255.0 172.17.13.1
Router(config)#ip route 172.17.15.0 255.255.255.0 172.17.11.1
Router(config)#ip route 172.17.11.0 255.255.255.252 172.17.12.1
Router(config)#no shut
Setingan pada router 3 :
Router>ena
Router#config
Configuring from terminal, memory, or network [terminal]?
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#interface fa0/0
Router(config-if)#ip address 172.17.14.1 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)#no shut
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up
Router(config-if)#exit
Router(config)#interface se2/0
Router(config-if)#ip address 172.17.10.2 255.255.255.252
Router(config-if)#clock rate 64000
Router(config-if)#no shut
Router(config-if)#exit
Router(config)#interface se3/0
Router(config-if)#ip address 172.17.13.1 255.255.255.252
Router(config-if)#clock rate 64000
Router(config-if)#no shut
Router(config-if)#exit
Router(config)#ip route 172.17.15.0 255.255.255.0 172.17.10.1
Router(config)#ip route 172.17.17.0 255.255.255.0 172.17.13.2
Router(config)#ip route 172.17.11.0 255.255.255.252 172.17.10.1
Router(config)#ip route 172.17.16.0 255.255.255.0 172.17.11.2
Router(config)#no shut.
Setelah selesai konfigurasi selanjutnya lakukan pengujian dengan cara melakukan ping seperti pada gambar berikut :
(Ping dari PC 0 ke Server 0)
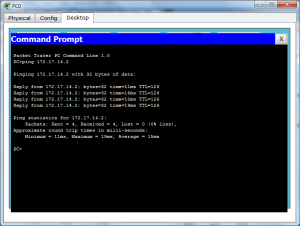
(Ping dari Server ke PC)
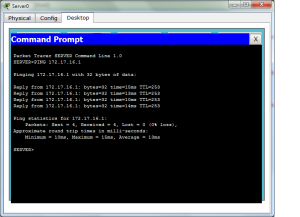
Lakukan pada seluruh PC agar koneksi benar-benar saling terhubung








 09.12
09.12
 bagas
bagas